Test der Sonneneinstrahlung
Sonnenstrahlung (UV-Strahlung) kann die Qualität von Produkten beeinflussen, wie etwa Verfärbung, Brüchigkeit und Elastizität von Materialien. Solar Radiation (UV)-Tests werden verwendet, um Geräte oder Komponenten unter UV-Strahlung zu testen. Die UV-Tests können mit Wassertests kombiniert werden, um die kombinierten Wettereinflüsse von Sonne und Regen zu simulieren.
Navigieren Sie zu:
→ Testübersicht
→ Maschinenspezifikationen testen
→ Normen
→ Gründe zum Testen
→ Theorie Beschleunigte Prüfung

Spektrum des Sonnenlichts
Das Sonnenspektrum ist die Sammlung von elektromagnetischen Wellenlängen, die von der Sonne ausgestrahlt werden und die Erde erreichen. Das Spektrum besteht aus drei wichtigen Komponenten:
280-400 nanometer (nm)
- Dieser Teil des Spektrums macht etwa 6,1 % der gesamten Sonnenenergie auf Meeresspiegelhöhe aus, was etwa 68 Watt/m² entspricht.
- UV-Strahlung wird weiter unterteilt in:
- UVA (315-400 nm): UVA-Strahlung kann erhebliche Auswirkungen auf Materialien wie Kunststoffe haben, da sie relativ energiereiche Strahlung ist, die tief in Materialien eindringen kann. Obwohl UVA weniger schädlich ist als UVB oder UVC, verursacht es über längere Zeit eine beschleunigte Alterung und Degradation von Kunststoffen.
- UVB (280-315 nm): UVB-Strahlung (280-315 Nanometer) kann einen erheblichen Einfluss auf Materialien haben, insbesondere auf deren physikalische und chemische Eigenschaften. Beispielsweise können Kunststoffe, die UVB ausgesetzt sind, allmählich abbauen aufgrund der Energie, die diese Strahlung im Material erzeugt.
- UVC (100-280 nm): Wird vollständig von der Atmosphäre absorbiert und erreicht die Erde nicht.
400-800 nm
- Dieser Teil macht etwa 51,8 % der gesamten Strahlung aus, mit einer Energie von etwa 580 Watt/m².
- Dies ist das Licht, das der Mensch sehen kann und ist verantwortlich für das sichtbare Farbspektrum.
800 nm und höher
- Infrarotstrahlung trägt am meisten zur Wärme bei, die wir von der Sonne spüren, und stellt den größten Teil der gesamten Strahlung dar.
Normen
Speziell ausgerichtet auf die Belichtung gegenüber Sonnenstrahlung (einschließlich UV-Strahlung).
Ziel der Norm
Das Ziel besteht darin, die Auswirkungen von Sonnenlicht, insbesondere des ultravioletten und sichtbaren Teils des Spektrums, zu simulieren. Dies ist entscheidend für Produkte, die langfristig im Freien verwendet werden oder intensiver Sonneneinstrahlung ausgesetzt sind.
Testmethode
- Spektrum: Der Test verwendet simuliertes Sonnenlicht (z. B. Xenon-Bogenlampen), um den UV- und sichtbaren Lichtteil des Sonnenlichtspektrums nachzubilden.
- Dauer: Die Testdauer und Intensität hängen von den Spezifikationen des zu testenden Produkts und der erwarteten Exposition während der Nutzung ab.
- Temperatur und Luftfeuchtigkeit: Diese Parameter können kontrolliert und variiert werden, um realistische Bedingungen zu schaffen.
Anwendungen
- Elektronische Geräte
- Kunststoffe, Beschichtungen und Farben
- Solarpanels
- Außeneinsätze wie Verkehrsschilder, Fahrzeugteile und Baumaterialien
Expositionstests
Die Norm legt fest, wie ein Produkt simuliertem Sonnenlicht ausgesetzt werden muss, um die Widerstandsfähigkeit gegenüber:
- Verfärbung
- Materialdegradation
- Rissen oder Bruch
- Funktionsverlust
Test der Sonneneinstrahlung
Testen Sie die Auswirkungen von UV- und Sonnenstrahlung auf Ihre Produkte mit unserem Solar Radiation Test.
Die UV-Tests können mit Wassertests kombiniert werden, um die kombinierten Wettereinflüsse von Sonne und Regen zu simulieren.

Spezifikationen der Testmaschinen in unserem Maschinenpark
Bei einem Test der Sonnenstrahlung misst und überwacht unser Suntester die Strahlung zwischen 300 nm und 800 Nanometern (UV+sichtbar). Die maximale Strahlung im Gerät beträgt 765 Watt/m² (UV+sichtbar), was 18 % höher ist als die maximale Sonneneinstrahlung auf Meereshöhe zur Mittagszeit am heißesten Tag des Sommers (ohne Wolken oder Luftverschmutzung). Für die Simulation von Sonnenlicht im Freien empfehlen die repräsentativsten Testmethoden einen Wert von 550 Watt/m². Für Simulationen hinter Fensterglas werden spezielle Filter verwendet, die UV-Strahlung ab 320 Nanometern durchlassen.
Spezifikationen
- Testbereichsgröße: 200 x 300 mm
- Temperaturbereich: 25 °C bis 60 °C
- Maximale Strahlung: 765 Watt/m² (300 - 800 Nanometer)
- Hinweis: Kombinierter Test mit UV+sichtbarem Licht und Wasser möglich
Theorie Beschleunigte Prüfung
Der SUNTESTER misst und überwacht Strahlung im Bereich von 300 nm bis 800 nm (UV + sichtbares Licht). Die maximale Strahlung im Gerät beträgt 765 Watt/m² (UV + sichtbares Licht), was 18 % höher ist als die maximale Sonnenstrahlung auf Meeresspiegelhöhe zur Mittagszeit.
- Extreme klimatische Bedingungen (hohe UV-Strahlung, heiß, trocken)
- Höhere Temperaturen als in Florida
- Minimale industrielle oder städtische Verschmutzung
- Historische Location (für „Automobil-Innenmaterialien“, der Standort mit der höchsten Belastung und zahlreichen verfügbaren Messungen und Studien)
Verschiedenen Studien zufolge können Sie also die Prüfung beschleunigen:
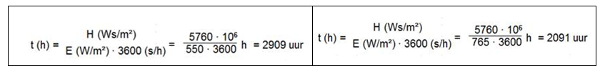
- 1 Jahr in Arizona (normale beschleunigte Alterung) = 2909 Stunden pro Jahr bei 550 Watt/m²
- 1 Jahr in Arizona (extreme beschleunigte Alterung) = 2091 Stunden pro Jahr bei 765 Watt/m²
- 1 Jahr in Europa (normale beschleunigte Alterung) = 1035 Stunden pro Jahr bei 550 Watt/m²
- 1 Jahr in Europa (extreme beschleunigte Alterung) = 744 Stunden pro Jahr bei 765 Watt/m²

4 gründe, warum Sie diese Tests durchführen lassen sollten:
Mit diesen Tests können Sie in nur zehn Tagen vorhersagen, wie sich Ihr Produkt nach der Sonneneinstrahlung und den Wettereinflüssen verhalten wird.
Dies spart Zeit und Kosten im Vergleich zu langwierigen Praxistests.
Bei Sebert Group ist es möglich, kombinierte Tests durchzuführen, die sowohl die Auswirkungen von Sonnenstrahlung als auch von Regen simulieren. Dies gibt einen vollständigen Überblick darüber, wie Ihr Produkt verschiedenen Wetterbedingungen standhält.
Durch das frühzeitige Testen der Auswirkungen von UV-Strahlung und anderen Wettereinflüssen können potenzielle Probleme wie Verfärbung, Brüchigkeit oder Verlust der Elastizität identifiziert und behoben werden, bevor das Produkt auf den Markt kommt.
Solar Radiation Tests sind für eine Vielzahl von Branchen relevant, wie die Automobil-, Bau-, Medizin- und Elektronikindustrie. Sebert Trillingstechniek verfügt über Erfahrung mit verschiedenen Produktarten und Materialien.
Do you have any questions?
Want to learn more about our testing methods or specific tests? Our experts are here to help with any inquiries you might have. Reach out today and find out how the Sebert Group can support you in delivering unmatched quality and reliability.
